Stress directly impacts your gut microbiota and disrupts dopamine production, affecting your mood, motivation, and mental health. Urban lifestyles, poor diets, and chronic stress have led to a 50% reduction in gut microbiome diversity over the last century, with 80% of urban residents reporting frequent gut-related issues. Here's what you need to know:
- Dopamine and Gut Health: Gut bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus are crucial for dopamine production, but stress reduces their populations.
- Stress Effects: Chronic stress triggers gut imbalances (dysbiosis), lowers beneficial bacteria, and increases inflammation, disrupting dopamine regulation.
- Solutions: Improve gut health with probiotics, prebiotics, fiber-rich diets, stress management, and quality sleep.
Quick Fixes for Gut-Dopamine Balance
- Supplements: Products like Begin Rebirth RE-1™ combine probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics to restore gut health.
- Diet: Eat 25–30 g of fiber daily and reduce processed foods.
- Lifestyle: Manage stress, improve sleep, and minimize toxin exposure.
A healthy gut is essential for mental and physical well-being. Addressing gut health can restore dopamine balance and break the stress cycle.
How Stress Affects The Gut
Stress Changes Gut Bacteria and Dopamine
Stress has a profound impact on both gut bacteria and dopamine production, linking our mental and physical health in surprising ways. Constant exposure to stress, especially in modern life, disrupts the gut's balance, leading to changes in bacterial populations and their role in dopamine production.
How Stress Impacts the Gut
When stress activates the body’s response system, it sets off a chain reaction that directly affects gut bacteria. This can lead to a condition called dysbiosis, where the gut's microbiome becomes imbalanced, impairing its ability to produce neurotransmitters like dopamine. Urban living, with its daily stressors, has been shown to reduce microbial diversity, weakening the gut's ability to regulate key functions.
Dopamine and Gut Bacteria
Certain bacterial strains in the gut are essential for producing and regulating dopamine. These include Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, which play key roles in maintaining healthy dopamine levels. Unfortunately, these beneficial bacteria are particularly sensitive to stress, and their populations often decline in stressful, urban environments.
Stress-related factors that can disrupt gut bacteria include:
| Stress Factor | Impact on Gut Bacteria |
|---|---|
| Chronic Stress | Reduces diversity and alters bacterial balance |
| Sleep Problems | Changes bacterial growth and activity |
| Environmental Toxins | Harms beneficial bacteria |
| Poor Diet | Limits nutrients bacteria need to thrive |
| Urban Living | Decreases exposure to natural bacterial sources |
This creates a vicious cycle: stress harms beneficial bacteria, reducing dopamine production, which can make individuals more sensitive to stress. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is crucial for both mental and physical health.
How Gut Bacteria Influence Dopamine
Bacteria and Dopamine Building Blocks
The gut microbiome plays an important role in creating the compounds needed for dopamine production. Certain bacteria break down dietary proteins into amino acids like tyrosine, which is a key building block for dopamine. Having a variety of gut bacteria is essential for making these precursors, which are critical for dopamine synthesis. A healthy gut microbiome also supports overall mental health and balance.
Bacterial Products and Brain Signals
Beyond producing precursors, gut bacteria influence brain signals through their metabolic byproducts. These bacteria release substances like short-chain fatty acids that can affect dopamine signaling. These compounds enter the bloodstream, interact with gut receptors, and ultimately impact the brain's dopamine release. However, modern urban lifestyles can disrupt this delicate communication between the gut and brain.
| Communication Pathway | Function | Impact on Dopamine |
|---|---|---|
| Short-chain Fatty Acids | Signal transmission | Helps regulate dopamine |
| Vagus Nerve Stimulation | Direct brain communication | Influences production |
| Immune System Signaling | Controls inflammation | Affects dopamine levels |
Gut Inflammation Effects on Dopamine
Inflammation in the gut can interfere with dopamine regulation. Urban living often leads to an imbalance in gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis, which disrupts the production of neurotransmitter precursors and weakens the gut's ability to manage inflammation. This, in turn, impacts dopamine signaling.
Targeted strategies to reduce gut inflammation - such as introducing specific bacterial strains - can help restore proper dopamine regulation. These approaches support the microbiome while also addressing immune and inflammatory challenges.
sbb-itb-1bbfe7f
Ways to Fix Gut and Dopamine Balance
Gut Health Supplements
Supplements can play a key role in restoring gut health and dopamine production. Products that combine prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics offer targeted support for the gut-brain connection.
For instance, Begin Rebirth RE-1™ is a 3-in-1 formula that delivers 500 billion CFU per serving and includes HOSt™ strains. In an observational study, 94% of participants reported less bloating and abdominal pain within just seven days of use.
While supplements like these are effective, pairing them with diet and lifestyle changes can provide even better results.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
Diet and lifestyle adjustments work hand-in-hand with supplements to improve gut health and dopamine balance. Here's how specific factors impact gut-brain health and what you can do:
| Factor | Impact on Gut-Brain Health | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Intake | Encourages growth of good bacteria | Eat 25–30 g of fiber daily |
| Processed Foods | Disrupts gut microbiome balance | Cut down on processed foods |
| Environmental Toxins | Harms gut barrier function | Minimize pesticide exposure |
| Stress Management | Alters gut bacteria composition | Practice relaxation techniques daily |
| Sleep Quality | Affects microbiome rhythms | Stick to a consistent sleep schedule |
Lifestyle changes can amplify the benefits of supplements. For example, Begin Rebirth RE-1™ also provides 4.5 g of prebiotic fiber (GOS & Inulin) per serving, which supports gut function.
Combining these dietary and lifestyle habits with targeted supplements creates a solid plan for improving gut health and dopamine levels.
Begin Rebirth RE-1™ Benefits
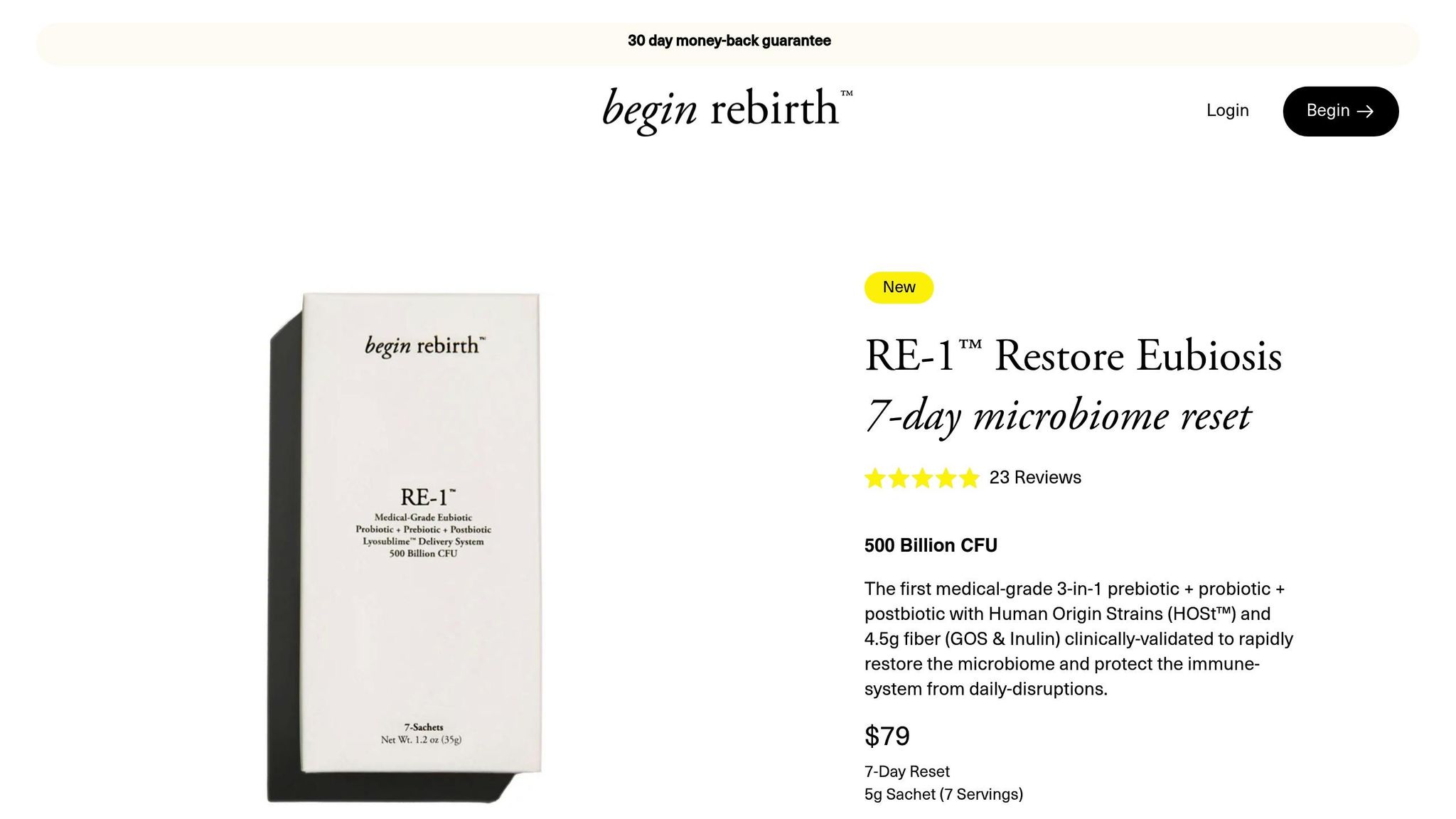
Begin Rebirth RE-1™ integrates both supplementation and lifestyle strategies to address gut and dopamine imbalances. Its Lyosublime™ delivery system ensures effective results. The product offers flexible options tailored to individual needs:
- 7-Day Reset ($79): Quick relief for symptoms
- 4-Week Protocol ($279): Helps maintain stability
- 3-Month Regimen ($739): Targets long-term imbalances
"This has been sincerely transformative for my gut health... Within days, I noticed reduced bloating and improved digestion. My appetite returned naturally, something I hadn't experienced in years... For anyone seeking relief from gut-related discomfort or immune support, this is truly the best choice. Highly recommended." – Simon S., Verified Buyer
Clinical data supports these claims, with 87% of users reporting fewer allergies and recurring infections after just one week of use.
Next Steps in Research
Current Research Gaps
Scientists are still uncovering the complexities of the gut-brain axis. While animal studies have shown encouraging outcomes, more human clinical trials are essential to confirm these findings. For instance, data reveals that 80% of urban residents are missing key Human Origin Strains (HOSt™), emphasizing the importance of targeted research in this area.
Here are some key areas needing further investigation:
| Research Area | Current Status | Future Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Strain Identification | Limited knowledge about specific bacterial effects | Mapping how each strain influences dopamine |
| Metabolite Analysis | Basic understanding of gut-brain pathways | In-depth study of bacterial metabolites and their role in mental health |
| Population Studies | Small and narrow sample sizes | Large-scale trials with diverse groups |
| Treatment Protocols | Generic methods being used | Developing tailored intervention strategies |
Individual Treatment Options
To address these gaps, researchers are exploring customized gut-based therapies. For example, Lactobacillus helveticus BR-MCC1848 may help prevent stress-induced depression, while Lactobacillus paracasei BR-MCC1849 could enhance infection resistance and improve mood under stress.
The focus is on understanding how prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics interact with unique gut microbiomes to create effective treatments.
Mental Health Treatment Updates
In addition to personalized therapies, there’s growing interest in integrating gut-focused approaches with traditional mental health treatments. This combined strategy shows potential for improving outcomes.
Key areas of focus include:
- Long-term Effects: Examining how gut microbiome therapies impact mental health over time.
- Combination Therapies: Studying how gut-targeted treatments work alongside existing mental health practices.
- Biomarker Development: Developing reliable tools to measure treatment success.
Evidence suggests that gut health could soon play a central role in mental health care, particularly for stress-related disorders.
Summary
Stress has a direct impact on gut microbiota, which in turn disrupts dopamine pathways. Urban stressors, in particular, play a major role in this imbalance. Over the past century, humans have reportedly lost around 50% of their gut microbiome, with 80% of people in urban areas experiencing daily gut-related issues.
Here’s a breakdown of the stress-gut-dopamine connection:
| Impact Area | Effect | Proposed Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Gut Microbiome | Urban stressors lead to dysbiosis | Reintroducing Human Origin Strains |
| Dopamine Production | Stress disrupts neurotransmitter levels | 3-in-1 eubiotic supplementation |
| Immune Function | Gut defenses are weakened by stress | High-potency probiotics (500B CFU) |
These findings highlight the need for clinical validation, and existing studies already back the effectiveness of these interventions.
Scientists are increasingly focused on personalized solutions for the gut-brain axis. One promising approach involves Human Origin Strains (HOSt™), which are identical to the strains humans are exposed to at birth. These strains could help restore gut balance and support dopamine function.
New research also highlights the importance of addressing the root causes of gut-brain imbalances. Targeted interventions, such as a 3-in-1 eubiotic strategy, aim to restore the microbiota-gut-brain axis rather than just managing symptoms. This underscores the importance of microbiome restoration in maintaining healthy dopamine pathways.